
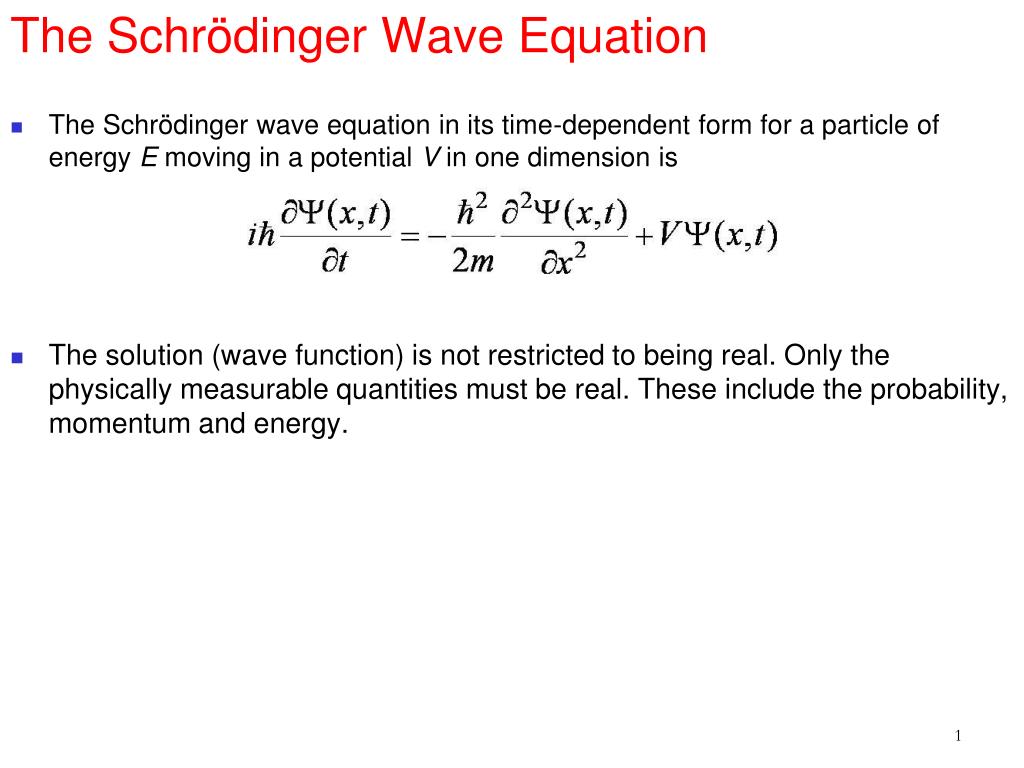
3.6: The Time-Dependent Schrodinger Equation The time-dependent Schrödinger equation, is used to find the time dependence of the wavefunction.Symbols for operators are often (although not always) denoted by a hat ^ over the symbol, unless the symbol is used exclusively for an operator. Of course, this is not done automatically you must do the work, or remember to use this operator properly in algebraic manipulations. 3.4: Operators, Eigenfunctions, Eigenvalues, and Eigenstates he Laplacian operator is called an operator because it does something to the function that follows: namely, it produces or generates the sum of the three second-derivatives of the function.In order to reach this objective, we need the appropriate wave equation.

3.3: Invention of the Schrödinger Equation Our goal as chemists is to seek a method for finding the wavefunctions that are appropriate for describing electrons, atoms, and molecules.We will consider a sine wave, take its first and second derivatives, and then examine the results. 3.2: A Classical Wave Equation The easiest way to find a differential equation that will provide wavefunctions as solutions is to start with a wavefunction and work backwards.Such thoughts may have motivated Erwin Schrödinger to argue that the wave equation is a key component of Quantum Mechanics.

This differential equation is called the wave equation, and the solution is called the wavefunction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
